Since proteins are constructed in the cytoplasm of the cell mRNA must cross the nuclear membrane to reach the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells. In eukaryotic translation 80S ribosomes with 40S and 60S subunits are used.
Learn more about microRNA -- the name of a family of molecules that helps cells control the kinds and amounts of proteins they make.
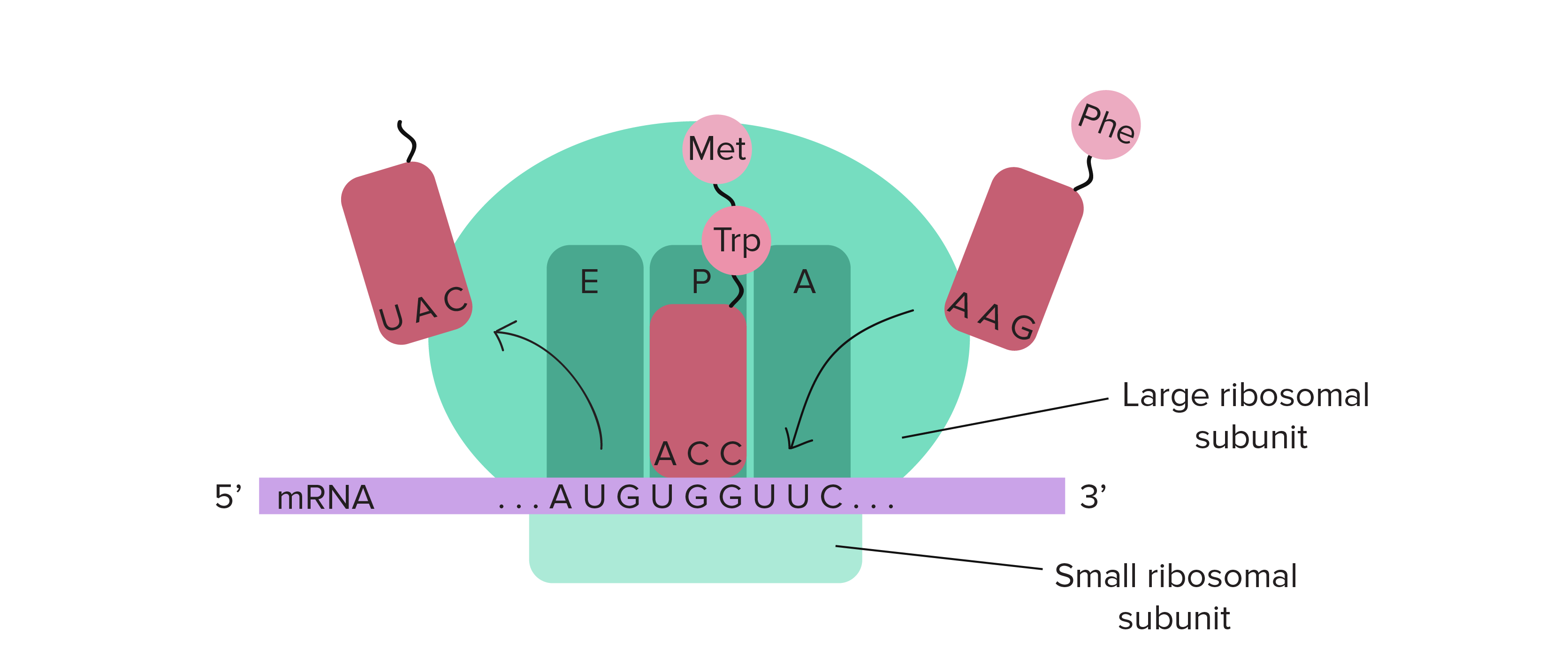
. Ribosomes are made of a small and large subunit which surrounds the mRNA. In eukaryotes there is single initiation and termination site. BA translation stop codon is added at the 3 end of the pre-mRNA c Coding sequences called exons are spliced out by ribosomes d Noncoding sequences called introns are spliced out by molecular complexes called spliceosomes e A poly-A tail 50-250 adenine nucleotides is added to the 3 end of the pre-mRNA.
After the first 20-30 nucleotides have been synthesized a cap consisting of a methylated guanine is added to the 5 end of the pre-mRNA. Assembly of the complete initiation complex releases RNA pol II which begins synthesizing the RNA transcript in the 5 3 direction. In translation the message coded in mRNA is converted into a protein.
This uses an mRNA sequence as a template to guide the synthesis of a chain of amino acids that form a. The mRNA is synthesized from DNA only. First three initiation factor proteins known as IF1 IF2 and IF3 bind to the small subunit of the.
The translation of mRNA begins with the formation of a complex on the mRNA Figure 4. Once in the cytoplasm ribosomes and another RNA molecule called transfer RNA work together.

Trnas And Ribosomes Article Translation Khan Academy

Ribosomes Transcription Translation Learn Science At Scitable


0 Comments